Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics
What’s the difference between micro and macro economics? These two economic disciplines can see confusing at first glance, but once you learn their focus it’s easy to differentiate microeconomic issues and questions from macroeconomic ones.
- Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Definitions
- Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Class
- Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Easier
- Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Pdf
- Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Pdf
In this blog post, you’ll learn the difference between micro and macro economics, as well as specific examples of micro and macro economic problems. Read on to learn the basics of microeconomic and macroeconomic thought, study and analysis.
Some of the most prominent uses of macroeconomics are to set the general price level for the products and to dealt with issues like inflation, poverty, and unemployment. Microeconomics vs. Microeconomics is the study of economics on the individual level, whereas macroeconomics is the study of economics on the national or global. Microeconomics is generally the study of individuals and business decisions, while macroeconomics looks at higher up country and government decisions. Education General. Macroeconomics vs Microeconomics – Key Differences ‘The difference’ is of course, that micro gives the picture from the smaller parts of the economy while macro looks at the economy at large. Other Differences.
Do you want to learn about micro and macro economics in greater detail? Enroll in our Micro & Macro Economics course to learn the specifics of economics, from basic principles of supply and demand the characteristics of the business cycle.
Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Definitions
Microeconomics vs. macroeconomics
The difference between micro and macro economics is simple. Microeconomics is the study of economics at an individual, group or company level. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, is the study of a national economy as a whole.
Microeconomics focuses on issues that affect individuals and companies. This could mean studying the supply and demand for a specific product, the production that an individual or business is capable of, or the effects of regulations on a business.
Macroeconomics focuses on issues that affect the economy as a whole. Some of the most common focuses of macroeconomics include unemployment rates, the gross domestic product of an economy, and the effects of exports and imports.
Does this make sense? While both fields of economics often use the same principles and formulas to solve problems, microeconomics is the study of economics at a far smaller scale, while macroeconomics is the study of large-scale economic issues.
Both fields of economics are interdependent
At first glance, micro and macro economics might seem completely different from one another. In reality, these two economic fields are remarkably similar, and the issues they study often overlap significantly.
For example, a common focus of macroeconomics is inflation and the cost of living for a specific economy. Inflation is caused by a variety of factors, ranging from low interest rates to expansion of the money supply.
While this might seem like a purely macroeconomic field of study, it’s actually one that’s very important in microeconomics. Since inflation raises the price of goods, services and commodities, it has serious effects for individuals and businesses.
On a microeconomic level, this has several effects. Businesses are forced to raise their prices in response to the increased cost of materials. They also need to pay their employees more over the long term to account for the higher cost of living.
Aficio MP C305SP/C305SPF. Microsoft Windows 10 (64-bit) Printer Driver; PCL 6 Driver. PCL6 Driver for Universal Print. Download (File Size: 26,535 KB) Ver.4.23.0.0 Released Date: New! Ricoh SAP Device Types for Barcode & OCR Package. Download (File Size: 18,593 KB). Download MP C305SPF driver from Ricoh Website How to Install Driver MP C305SPF for Windows. Download the Drivers or Software and select the location of the files which have been saved. Double-click the.exe file extension is available in the download location, and the Setup screen will be displayed. Compared with using 'PCL6 Driver for Universal Print' by itself, this utility provides users with a more convenient method of mobile printing. Note: PCL6 Driver for Universal Print v2.0 or later can be used with this utility. Earlier versions or other printer drivers cannot be used with this utility. Sep 07, 2015 MP C305SP/C305SPF Sign up: Software Release Notifications. Printer Driver Packager NX Printer Driver Editor GlobalScan NX RICOH Streamline NX Card Authentication Package Network Device Management Web SmartDeviceMonitor Remote Communication Gate S. Ricoh MP C305SP Driver Downloads Printer driver for B/W printing and Color printing in Windows. It supports HP PCL XL commands and is optimized for the Windows GDI. High performance printing can be. Savin mp c305spf driver.
This is just one example of a macroeconomic phenomenon – in this case, inflation and a rising cost of living – affecting a microeconomic one. Other macroeconomic decisions, such as the creation of a minimum wage or tariffs for certain goods and materials, have significant microeconomic effects.
Do you want to gain a detailed understanding of macroeconomics? Enroll in our Economics Without Borders course to learn how currencies, central banks and a wide variety of other factors affect national and global economies.
Examples of microeconomic issues
Microeconomics seeks to solve problems on a small level. Some economics like to describe microeconomics as the study of economics and behavior from the bottom up, since it’s focused on the effects of low-level decisions on the economy.
An example of a microeconomic issue could be the effects of raising wages within a business. If a large business raises its wages by 10 percent across the board, what is the effect of this policy on the pricing of its products going to be?
Since the cost of producing products has increased, the price of these products for consumers is likely to follow suit. Likewise, what will happen if a company raises wages for its most productive employees but fires its least productive workers?
These are the type of questions microeconomics aims to solve. Microeconomics is also useful for studying the effects of your own decisions. One of the most common principles in microeconomics is opportunity cost.
Opportunity cost is the value of making one decision over another. A decision that involves economy cost is the choice of one meal instead of another: by choosing a certain food, you miss out on the benefits offered by another.
Choices involving opportunity cost could relate to your career. By choosing one job over another, you may gain opportunities but lose others. In addition to factors like supply and demand, opportunity cost is one of the principles of microeconomics.
Learn more about opportunity cost, including several examples of the opportunity cost of career choices and buying decisions, in our blog post on the opportunity cost formula.
Due to the narrow focus of macroeconomics, it’s an incredibly valuable skillset for making decisions in your own life. Learn more about intelligent decision making in our Cognitive Biases: Learn to Master Decision Making course.
Examples of macroeconomic issues
While microeconomics focuses on the effects a certain decision has on individuals and businesses, macroeconomics looks at the bigger picture. In macroeconomics, a common issue is the effects of certain policies on the national or regional economy.
For example, while a microeconomist might study the effects of low interest rates on individual borrowers, a macroeconomist would observe the effects that low interest rates have on the national housing market or the unemployment rate.
Another common focus of macroeconomics is the way taxes affect the economics of a nation. A macroeconomist would look at the effects of a decrease in income taxes using measures like GDP and national income, rather than individual factors.
Do you want to learn more about macroeconomics? Discover how interest rates and trade policy affects the national economy by enrolling in our 21st century economics course, How The Economy Really Works.
The importance of a balanced economics education
Microeconomics and macroeconomics have a lot in common, and the skills used to solve small-scale economic issues are often identical to those used to find solutions to large-scale economic problems.
Learn the impact of economic variables on small firms, individuals, households and the economy as a whole in our Micro & Macro Economics course. Designed for new economics students, this in-depth course is an excellent introduction to macro and micro economics.
Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics: An Overview
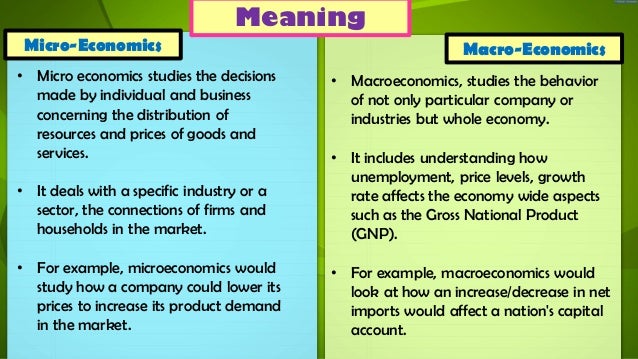
Economics is divided into two different categories: microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics is the study of individuals and business decisions, while macroeconomics looks at the decisions of countries and governments.
While these two branches of economics appear to be different, they are actually interdependent and complement one another since there are many overlapping issues between the two fields.
Microeconomics
Microeconomics is the study of decisions made by people and businesses regarding the allocation of resources and prices of goods and services. It also takes into account taxes and regulations created by governments.
Microeconomics focuses on supply and demand and other forces that determine the price levels in the economy. It takes what is referred to as a bottom-up approach to analyzing the economy. In other words, microeconomics tries to understand human choices and resource allocation.
Having said that, microeconomics does not try to answer or explain what forces should take place in a market. Rather, it tries to explain what happens when there are changes in certain conditions.
For example, microeconomics examines how a company could maximize its production and capacity so that it could lower prices and better compete in its industry. A lot of microeconomic information can be gleaned from the financial statements.
Microeconomics involves several key principles including (but not limited to):
- Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium: Prices are determined by the theory of supply and demand. Under this theory, suppliers offer the same price demanded by consumers in a perfectly competitive market. This creates economic equilibrium.
- Production Theory: This is the study of production.
- Costs of Production: According to this theory, the price of goods or services is determined by the cost of the resources used during production.
- Labor Economics: This principle looks at workers and employers, and tries to understand the pattern of wages, employment, and income.
The rules in microeconomics flow from a set of compatible laws and theorems, rather than beginning with empirical study.
Microeconomics Vs. Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics, on the other hand, studies the behavior of a country and how its policies affect the economy as a whole. It analyzes entire industries and economies, rather than individuals or specific companies, which is why it's a top-down approach. It tries to answer questions like 'What should the rate of inflation be?' or 'What stimulates economic growth?'
Macroeconomics examines economy-wide phenomena such as gross domestic product (GDP) and how it is affected by changes in unemployment, national income, rate of growth, and price levels.
Macroeconomics analyzes how an increase or decrease in net exports affects a nation's capital account, or how GDP would be affected by the unemployment rate.
Macroeconomics focuses on aggregates and econometric correlations, which is why it is used by governments and their agencies to construct economic and fiscal policy. Investors of mutual funds or interest rate-sensitive securities should keep an eye on monetary and fiscal policy. Outside of a few meaningful and measurable impacts, macroeconomics doesn't offer much for specific investments.
John Maynard Keynes is often credited as the founder of macroeconomics, as he initiated the use of monetary aggregates to study broad phenomena. Some economists dispute his theory, while many of those who use it disagree on how to interpret it.
Investors and Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics
Individual investors may be better off focusing on microeconomics than macroeconomics. There may be some disagreement between fundamental (particularly value) and technical investors about the proper role of economic analysis, but it is more likely that microeconomics will affect an individual investment proposal.
Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Class
Warren Buffettfamously stated that macroeconomic forecasts don't influence his investing decisions. When asked about how he and business partner Charlie Munger choose investments, Buffett responded, 'Charlie and I don't pay attention to macro forecasts. We've worked together for 50+ years, and I can't think of a time when they influenced a decision about stock or a company.' Buffett also referred to macroeconomic literature as 'the funny papers.'
Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Easier
John Templeton, another famously successful value investor who died in 2008 at the age of 95, shared a similar sentiment. 'I never ask if the market is going to go up or down because I don't know. It doesn't matter. I search nation after nation for stocks, asking: 'where is the one that is lowest priced in relation to what I believe it's worth?' said Templeton.
Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Pdf
Key Takeaways
Microeconomics Vs Macroeconomics Pdf
- Microeconomics studies individuals and business decisions, while macroeconomics analyzes the decisions made by countries and governments.
- Microeconomics focuses on supply and demand, and other forces that determine price levels, making it a bottom-up approach.
- Macroeconomics takes a top-down approach and looks at the economy as a whole, trying to determine what the economy should look like.
- Investors can use microeconomics in their investment decisions, while macroeconomics is an analytical tool mainly used to craft economic and fiscal policy.